resultant displacement|resultant displacement physics : Tuguegarao Apply analytical methods of vector algebra to find resultant vectors and to solve vector equations for unknown vectors. Interpret physical situations in terms of vector .
One of Cagayan De Oro’s most popular attractions is an amusement park that’s perfect for both children and adults. Larry’s Hill Adventure Hub is a huge playground that offers a wide array of activities that will surely entertain guests of all ages!
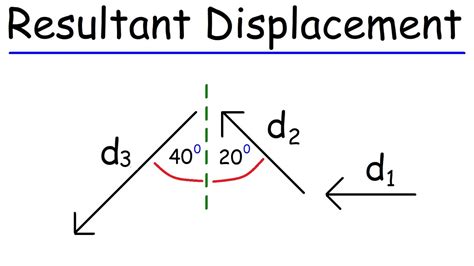
resultant displacement,Make the lengths proportional to the distance of the given displacement and orient the arrows as specified relative to an east-west line. Use the head-to-tail method outlined above to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement, which we’ll call R.resultant displacement physicsThe resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will .Resultant Displacement - Vectors. The Organic Chemistry Tutor. 7.23M subscribers. Subscribed. 972. 64K views 1 year ago New Physics Video Playlist. This physics video .
The displacement is 10.3 blocks at an angle 29 .1º north of east. Figure 3.9 To describe the resultant vector for the person walking in a city considered in Figure 3.8 graphically, .What is a Resultant? Vector Components. Vector Resolution. Component Addition. Relative Velocity and River Boat Problems. Independence of Perpendicular Components of Motion. Earlier in this lesson, we learned .Apply analytical methods of vector algebra to find resultant vectors and to solve vector equations for unknown vectors. Interpret physical situations in terms of vector .
The head-to-tail method outlined above will give a way to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement, denoted . Solution (1) Draw .

Calculate the velocity vector given the position vector as a function of time. Calculate the average velocity in multiple dimensions. Displacement and velocity in two .
How to Find Resultant Displacement in Physics : Physics & Math. eHowEducation. 305K subscribers. 67K views 10 years ago Physics & Math. .more. Subscribe.
The horizontal displacement of the projectile is called the range of the projectile and depends on the initial velocity of the object. . Resultant force on Earth’s surface, of the attraction by the Earth’s masses, and the centrifugal pseudo-force caused by .
resultant displacement resultant displacement physicsThe horizontal displacement of the projectile is called the range of the projectile and depends on the initial velocity of the object. . Resultant force on Earth’s surface, of the attraction by the Earth’s masses, and the centrifugal pseudo-force caused by .The head-to-tail method outlined above will give a way to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement, denoted R R. Solution (1) Draw the three displacement vectors. Figure 3.14 (2) Place the vectors head to tail retaining both their initial magnitude and direction. Figure 3.15Resultant displacement and vector addition have various real-life applications in mathematics education. One example is in navigation, where the resultant displacement can be used to determine the shortest distance between two points or to calculate the direction and magnitude of a ship or airplane's movement. Another application is in .The resultant displacement is the vector sum of the two displacements experienced during the trip. Since they're perpendicular to one another, the resultant is the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Its magnitude can be found using pythagorean theorem and its direction can be found using the tangent function.

The result (or resultant) of walking 11 km north and 11 km east is a vector directed northeast as shown in the diagram to the right. Since the northward displacement and the eastward displacement are at right angles to each other, the Pythagorean theorem can be used to determine the resultant (i.e., the hypotenuse of the right triangle). The head-to-tail method outlined above will give a way to determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement, denoted . Solution. (1) Draw the three displacement vectors. Figure 3.3.8 3.3. 8. (2) Place the vectors head to tail retaining both their initial magnitude and direction. Figure 3.3.9 3.3. 9.We resolve each displacement vector to its scalar components and substitute the components into Equation 2.25 to obtain the scalar components of the resultant displacement D → D → from the lodge to the rest point. On the way back from the rest point to the lodge, the displacement is B → = − D → B → = − D →.resultant displacementThe resultant is the vector sum of two or more vectors. It is the result of adding two or more vectors together. If displacement vectors A, B, and C are added together, the result will be vector R. As shown in the diagram, vector R can be determined by the use of an accurately drawn, scaled, vector addition diagram.. To say that vector R is the resultant . The resultant displacement formula is used when the distance from the point of reference is used to specify the initial and final position of the object. Despite the fact that distance and displacement are not the same things, displacement problems will tell you how many “foot” or “meters” an object has travelled. Problems would also .The Principle of Superposition. The principle of superposition states that: When two or more waves meet, the resultant displacement is the vector sum of the displacements of the individual waves. This principle describes how waves which meet at a point in space interact. When two waves with the same frequency and amplitude arrive at a point .The first answer was correct, displacement does need a quantity and direction. Displacement can be calculated by measuring the final distance away from a point, and then subtracting the initial distance. Displacement is key when determining velocity (which is also a vector). Velocity = displacement/time whereas speed is distance/time.The resultant displacement is the vector d, the sum of two vectors d 1 and d 2 which point in opposite directions. Details of the calculation: The sum of the two displacement vectors is d = d 1 + d 1 = (-110 m) + 25 m = -85 m. .
Finding the Resultant of Two Displacements. We can use vectors to find direction, velocity, and force of moving objects. In this section we will look at a few applications where we will use resultants of vectors to find speed, direction, and other quantities. A displacement is a distance considered as a vector.The resultant displacement is the vector d, the sum of two vectors d 1 and d 2 which point in opposite directions. Details of the calculation: Thee sum of the two displacement vectors is d = d 1 + d 1 = (-110 m) + 25 m = -85 m. You can also argue in the following way. For the total displacement it only matters where you start and where you stop.
To find the magnitude of the resultant displacement, we can treat the student's movements as vectors and use vector addition. The displacement in the east direction is a vector of +1.0 kilometers, the displacement in the south direction is a vector of -1.0 kilometers, and the displacement in the west direction is a vector of -2.0 kilometers.
resultant displacement|resultant displacement physics
PH0 · resultant displacement vector
PH1 · resultant displacement physics
PH2 · resultant displacement formula
PH3 · resultant displacement definition
PH4 · resultant displacement calculator
PH5 · formula to find displacement
PH6 · calculate total displacement
PH7 · calculate displacement
PH8 · Iba pa